Scale and Distribute
In the previous tutorial, we chose a capability provider and deployed a simple application. Now we'll learn how to scale and distribute a wasmCloud application.
This tutorial assumes you're following directly from the previous steps. Make sure to complete Quickstart, Add Features, and Extend and Deploy first.
Scaling up 📈
WebAssembly can be easily scaled due to its small size, portability, and wasmtime's ability to efficiently instantiate multiple instances of a single WebAssembly component. We leverage these aspects to make it simple to scale your applications with wasmCloud. Components only use resources when they're actively processing requests, so you can specify the number of replicas you want to run and wasmCloud will automatically scale up and down to meet demand.
Let's scale up our hello world application to 100 replicas by editing wadm.yaml:
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: hello-world
annotations:
description: 'HTTP hello world demo using the WebAssembly Component Model and WebAssembly Interfaces Types (WIT)'
spec:
components:
- name: http-component
type: component
properties:
image: ghcr.io/wasmcloud/components/http-hello-world-rust:0.1.0
traits:
- type: spreadscaler
properties:
# Update the scale to 100
replicas: 100
Now your hello application is ready to deploy v0.0.3 with 100 replicas, meaning it can handle up to 100 concurrent incoming HTTP requests. Just run wash app deploy wadm.yaml again, wasmCloud will be configured to automatically scale your component based on incoming load.
Distribute Globally 🌍
No matter where your components and capability providers run, they can seamlessly communicate on the lattice. This means you can deploy your components to any cloud provider, edge location, or even on-premises and they will be able to communicate with each other. This is possible because wasmCloud uses NATS as its messaging layer, which is a lightweight, high-performance, and secure messaging system that can be deployed anywhere.
Distributing your application just requires updating your manifest to include spread information and making sure there are available wasmCloud hosts in the desired locations. We can update our hello application to run in multiple locations by editing wadm.yaml:
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: hello-world
annotations:
description: 'HTTP hello world demo using the WebAssembly Component Model and WebAssembly Interfaces Types (WIT)'
spec:
components:
- name: http-component
type: component
properties:
image: ghcr.io/wasmcloud/components/http-hello-world-rust:0.1.0
traits:
- type: spreadscaler
properties:
replicas: 100
# Ensure the component is spread across multiple zones
# Of the 100 replicas, place 80% in us-east-1 and 20% in us-west-1
spread:
- name: eastcoast
weight: 80
requirements:
zone: us-east-1
- name: westcoast
weight: 20
requirements:
zone: us-west-1
These requirements will ensure that 80% of the replicas are placed in us-east-1 and 20% in us-west-1. You can specify any number of zones and weights to distribute your components across multiple locations. Each requirement matches directly with a label that must be present on a host, and your currently launched host doesn't have any specified labels. Let's launch two more hosts with the required labels, and then deploy our new application.
If you already deployed your application, it will be placed in the Failed state because the requirements are not met. As soon as we launch the hosts with the required labels, the application will be automatically rescheduled.
wash up --multi-local --label zone=us-east-1 -d
wash up --multi-local --label zone=us-west-1 -d
Just run wash app deploy wadm.yaml again, wasmCloud will be configured to automatically distribute your component across multiple locations based on the spread requirements. You can see all of your hosts and the components running on them by running wash get inventory.
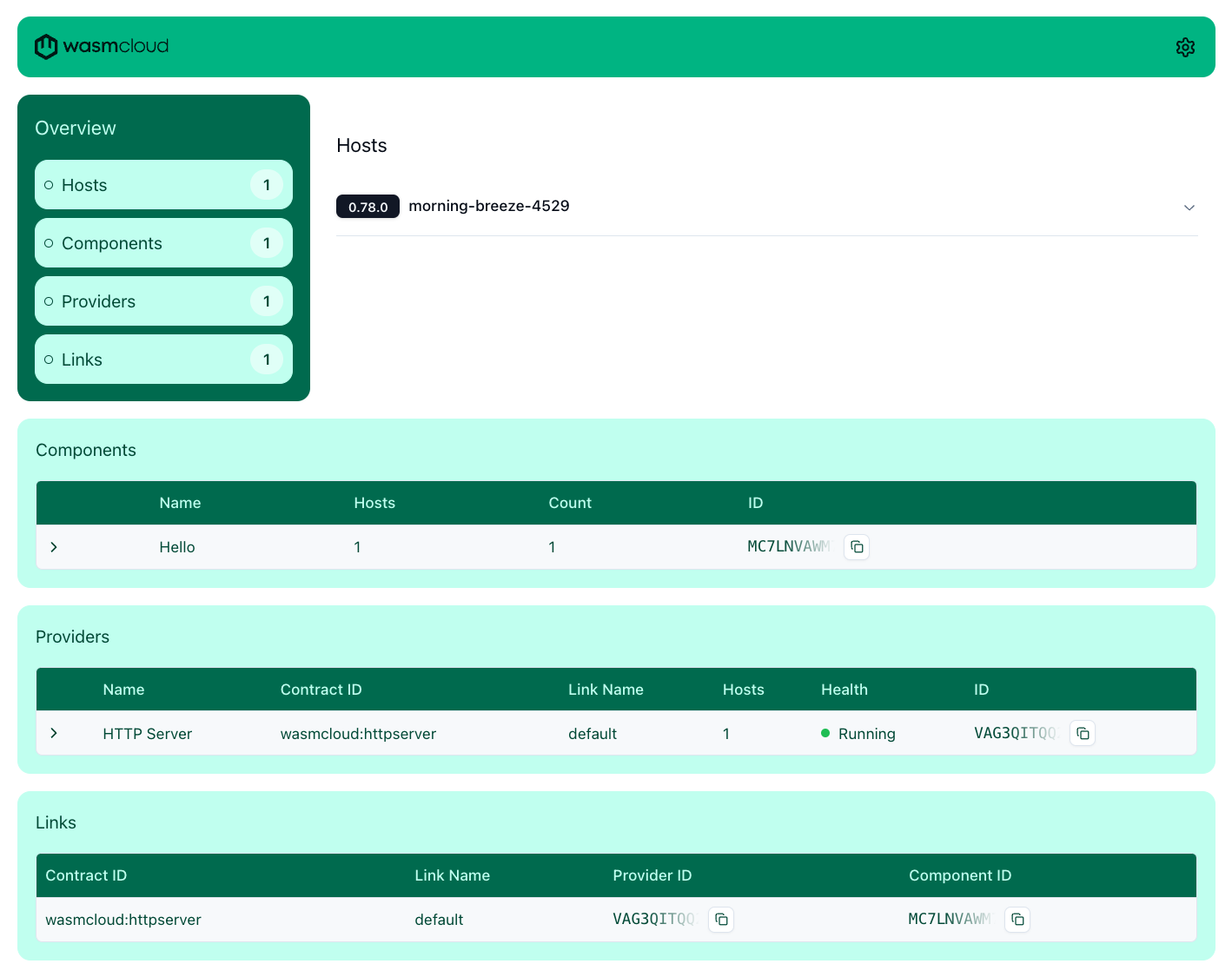
View the wasmCloud dashboard
You can start the wasmCloud dashboard using the wash.
wash ui
If you would like to change the port that the websocket is enabled on, you can pass the --nats-websocket-port option to wash up.
Note that you will need to stop NATS if it is already running or the new config will not apply. You can do this with wash down --all to stop everything.
wash up --nats-websocket-port 4444 # defaults to 4223
Treat wasmCloud hosts as commodity. Stopping your host will stop all of the components running on it, and wadm will look for other available hosts to reschedule your application on. As soon as you launch your new host with the --nats-websocket-port option, your application will be rescheduled on it and work just as it did before.
Then, you can launch the wasmCloud dashboard using wash ui, which will launch the dashboard on http://localhost:3030.
This is a great way to visualize what is running on your host, even multiple hosts that are connected to the same NATS server.
Summary
Now you've learned how to scale your applications with wasmCloud and distribute them across multiple locations. You can use this same approach to scale and distribute any wasmCloud application based on load and location requirements. Read on to the next page to learn more about the benefits of wasmCloud and how to continue to develop after this quickstart.